Table of Contents
In the high-stakes world of modern development, time is the only currency that matters more than money. For decades, the industry has been plagued by weather delays, labor shortages, and budget overruns. But a solution has emerged that is not just a “band-aid” but a complete surgical reconstruction of how we build. This solution is Modular & Prefab Construction.
As we move through 2025, this methodology is no longer an “alternative” choice; it is becoming the standard for efficiency. From emergency housing deployed in weeks to 44-story skyscrapers erected in months, Modular & Prefab Construction is proving that we can build faster, cleaner, and smarter.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dismantle the myths, explore the cutting-edge “Design for Manufacture and Assembly” (DfMA) technology, and analyze the real-world case studies that are proving the skeptics wrong.
Defining the Revolution: Modular vs. Prefab
Before we dive into the technology, we must clarify the terminology, as Modular & Prefab Construction are often used interchangeably, though they mean slightly different things.
- Prefabrication (Prefab): This is the umbrella term. It refers to any building component made off-site in a factory and transported to the site. This could be a wall panel, a roof truss, or a bathroom pod.
- Modular Construction: This is a specific type of prefabrication. It involves building entire 3D volumetric sections (modules)—complete with electrical wiring, plumbing, and interior finishes—in a factory. These modules are then stacked like LEGO bricks on-site to form a complete building.
The “Parallel Processing” Advantage
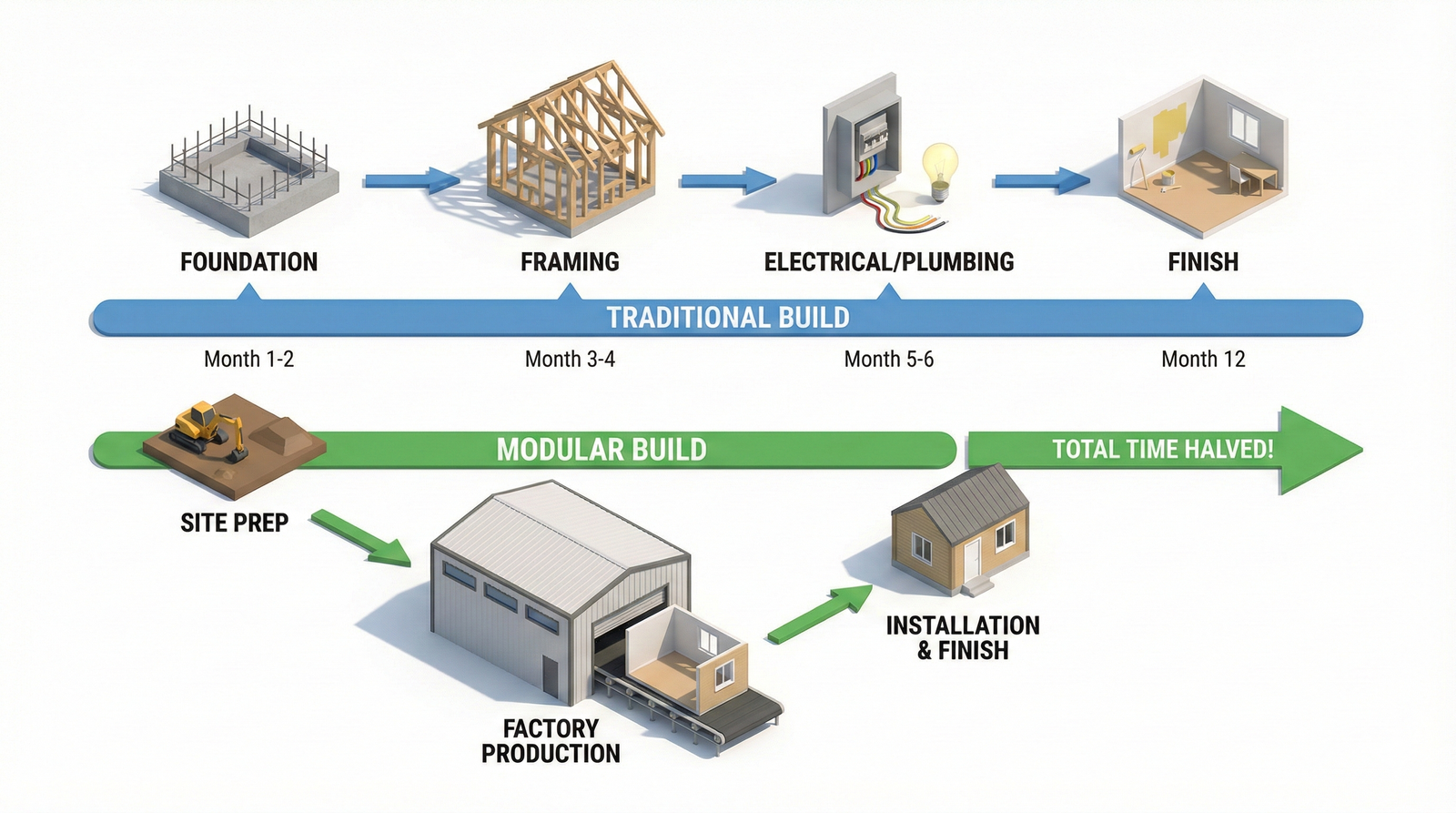
The secret sauce of Modular & Prefab Construction is “parallel processing.” In traditional construction, you cannot frame the second floor until the foundation is cured. It is a linear, slow process.
In modular construction, the building is being manufactured in a factory at the same time the foundation is being poured on-site. This overlapping schedule is what allows for project timelines to be reduced by 30% to 50%.
The Tech Behind the Speed: DfMA and Digital Fabrication
You cannot build at 2025 speeds using 1990s tools. The engine driving Modular & Prefab Construction is a methodology called DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly).
DfMA shifts the mindset from “how do we build this?” to “how do we manufacture this?” It treats a building like a product—an iPhone or a Tesla—rather than a one-off art project.
The Software Ecosystem
Architects and engineers are now using a specific suite of tools to enable this:
- Autodesk Revit + Strucsoft: For automating the detailing of light gauge steel (LGS) or wood framing directly from the BIM model to the CNC machines in the factory.
- hsbcad: The industry leader for timber construction, allowing for precise “file-to-factory” workflows where every screw hole is pre-drilled by robots.
- ArchiLabs & AI Agents: New for 2025, AI-driven plugins are now auto-generating optimized floor plans that minimize waste and maximize module transport efficiency.
By using these tools, Modular & Prefab Construction eliminates the “measure twice, cut once” error margin. The laser cuts it once, perfectly, every time.


Real-World Case Studies: The Giants of Efficiency
Theory is great, but let’s look at the buildings that are proving Modular & Prefab Construction works at scale.
1. Ten Degrees Croydon: The Vertical Village
Standing at 135 meters tall, Ten Degrees in Croydon, London, is a monument to modular capability. It is the world’s tallest modular residential building.
- The Stats: 44 stories, 546 homes.
- The Speed: The project was completed in just 26 months.
- The Method: Vision Modular Systems manufactured the apartments off-site. By the time the concrete core reached the 20th floor, the modules for the lower floors were already being craned into place, fully finished with kitchens and bathrooms installed.
2. CitizenM Hotels: The 5-Week Miracle
CitizenM has built its entire global brand on Modular & Prefab Construction. Their hotels are famous for consistent high quality because every room is identical and built on an assembly line.
- The Tech: They utilize a “Hollo-Bolt” system that allows modules to be blind-bolted together without on-site welding.
- The Result: For their Seattle and London projects, the on-site assembly of the modules took as little as 5 weeks, compared to the 6-8 months required for traditional framing and fit-out.
3. Emergency Housing: A Lifeline in 2025
In 2024 and early 2025, we saw Modular & Prefab Construction deployed for rapid disaster relief. Following the Los Angeles wildfires and Hurricane Helene recovery efforts, modular units were deployed to provide permanent-quality housing in temporary timeframes. Projects like the Modular Bridge Housing in Peterborough and Montreal have also used these methods to create dignified, insulated, and private homes for the homeless in a fraction of the time it takes to build shelters.

The Cost Equation: Is It Actually Cheaper?
This is the most common question. The answer is nuanced.
- Upfront Cost: Modular & Prefab Construction can be more expensive upfront. You have to pay for the factory time and materials before construction begins.
- Overall Cost: It is usually cheaper in the long run. Why?
- Reduced Financing: If you finish a hotel 6 months early, that is 6 months of extra revenue and 6 months of saved interest payments on your construction loan.
- Waste Reduction: Factories reduce material waste by up to 50%. You aren’t paying for cut-off lumber that ends up in a dumpster.
- Labor Efficiency: Factory labor is often cheaper and safer than on-site trade labor, and weather delays (which burn money) are non-existent indoors.
The Future: 3D Printing and Living Modules
As we look beyond 2025, Modular & Prefab Construction is merging with 3D concrete printing. Companies are now experimenting with “hybrid modules”—a 3D printed concrete core for strength/plumbing, wrapped in light prefabricated panels for insulation.
We are also seeing the rise of “circular modules.” These are buildings designed to be disassembled. In 50 years, instead of demolishing the building, you simply unbolt the modules and move them to a new city or recycle them.

Conclusion
Modular & Prefab Construction is not a trend; it is the industrial revolution finally catching up with the built environment. It offers the only viable path to meeting the global demand for housing and infrastructure without bankrupting the planet or the developer.
For those willing to adapt to the DfMA workflow and embrace the factory floor, the rewards are clear: faster delivery, higher quality, and a smarter way to build the world.
FAQ
Are modular buildings as strong as traditional buildings?
Yes, often stronger. Modular & Prefab Construction units are engineered to withstand the stresses of transportation (being bouncing on a truck) and lifting by a crane. This means they often contain more structural material than a standard site-built home.
Can I customize a modular building, or do they all look the same?
Customization is high, but it happens early. With tools like Revit and DfMA software, you can design almost anything. However, once the design is sent to the factory, changes are expensive. The “cookie-cutter” reputation is outdated; modern modular buildings like Ten Degrees feature complex, beautiful facades.
How much time does Modular & Prefab Construction save?
On average, it saves 30% to 50% of the total project schedule. This is largely because site preparation (foundation, utilities) happens simultaneously with the manufacturing of the building modules.
Is financing harder for modular projects?
It can be. Traditional banks release funds as work is completed on-site. In Modular & Prefab Construction, a large chunk of cash is needed upfront to pay the factory before the modules arrive on site. However, more lenders in 2025 are adapting to “off-site construction” loan products.
What is the lifespan of a modular building?
The same as a traditional building—50 to 100 years or more. These are permanent structures built to the same (or stricter) building codes as conventional construction.